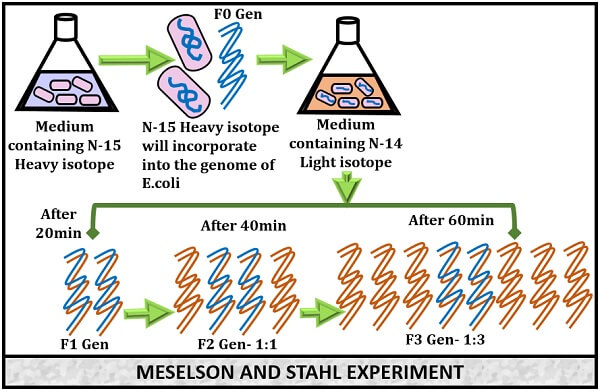
Meselson Stahl Experiment
The Nirenberg and Matthaei experiment was a scientific experiment performed in May 1961 by Marshall W. At the end of every duplication event all DNA molecules carry one parental strand and one strand newly created from nucleotide polymerization.
Meselson And Stahl Experiment Definition Steps Conclusion Biology Reader
Griffiths findings were followed by research in the late 1930s and early 40s that isolated DNA as the material that communicated this genetic information.

. Heinrich Matthaei at the National Institutes of Health NIH. DNA samples were then separated via. When 14 N was.
The second is that visible light can be transformed into infrared energy by being absorbed and re-emitted at Earths surface. Griffiths experiment reported in 1928 by Frederick Griffith was the first experiment suggesting that bacteria are capable of transferring genetic information through a process known as transformation. A series of elegant experiments by Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl with help from Mason MacDonald and Amandeep Sehmbi supported the idea that DNA replication was in fact semi-conservative.
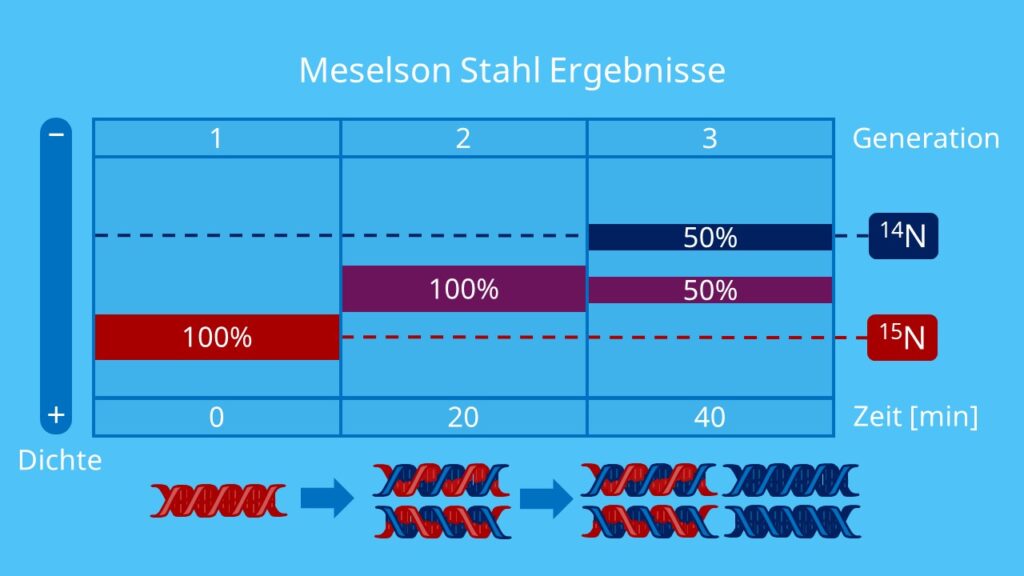
Nitrogen-15 15 N and nitrogen-14 14 N. 米西尔逊-斯塔尔实验 1 Meselson-Stahl experiment 米西尔逊-斯塔尔实验 3张 如果半保守复制是正确的则新生DNA双链中的一条链应该是新合成的而另一条链应该是全部从亲代接受继承的旧链. DNA replication and RNA transcription and translation.
Aprenda Matemática Artes Programação de Computadores Economia Física Química Biologia Medicina Finanças História e muito mais gratuitamente. Meselson and Stahl opted for nitrogen because it is an essential chemical component of DNA. A key historical experiment that demonstrated the semi-conservative mechanism of DNA replication.
DNA molecules were prepared using the heavier 15 N and then induced to replicate in the presence of the lighter 14 N. The experiment used water H 2 O methane CH 4 ammonia NH 3 hydrogen H 2 and. Still by conducting this thought experiment Fourier identified two important features of the greenhouse effect.
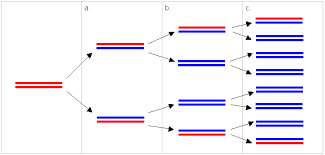
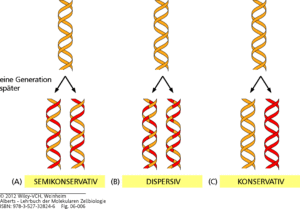
Meselson and Stahl were able to experimentally test the validity of these three models using radioactive isotopes of nitrogen. Nirenberg and his post-doctoral fellow J. Das Meselson und Stahl Experiment zeigte dass der Mechanismus einer semikonservativen Replikation entsprechen muss.
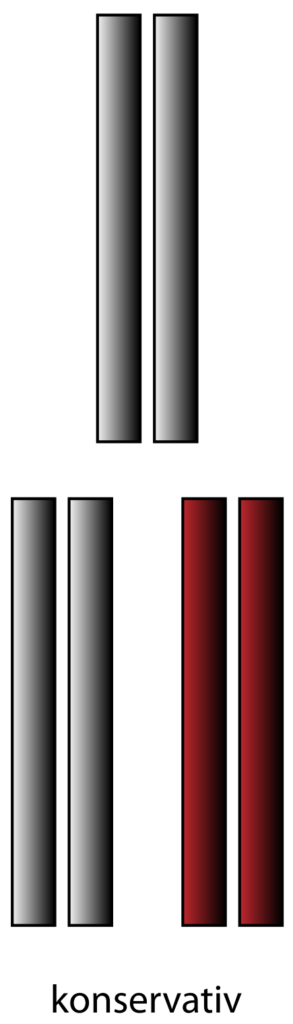
Meselson and Stahl experiment gave the experimental evidence of DNA replication to be semi-conservative typeIt was introduced by the Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl in the year 1958Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl have used Ecoli as the Model organism to explain the semiconservative mode of replication. Mode of DNA replication. There are three modes of replication introduced.
The first is that the atmosphere is basically transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared energy. The Meselson-Stahl experiment stemmed from a debate in the 1950s among scientists about how DNA replicated or copied itself. A Khan Academy é uma organização sem fins lucrativos com a missão de oferecer ensino de qualidade gratuito para qualquer pessoa em qualquer lugar.
Please contact Savvas Learning Company for product support. This is the simplistic DNA RNA protein pathway published by James Watson in the first edition of The Molecular Biology of the Gene 1965. Therefore every time a cell divides and its DNA replicates it incorporates new N atoms into the DNA of.
While the dogma as originally stated. El experimento de Meselson - Stahl fue un experimento realizado en 1957 por Matthew Meselson y Franklin Stahl en el que se demostró que la replicación de ADN era semiconservadoraUna replicación semiconservadora es aquella en que la cadena de dos filamentos en hélice del ADN se replica de forma tal que cada una de las dos cadenas de ADN. The debate began when James Watson and Francis Crick at the University of Cambridge in Cambridge England published a paper on the genetic implications of their proposed structure of DNA in May 1953.
Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Watsons version differs from Cricks because Watson describes a two-step DNA RNA and RNA protein process as the central dogma. The semiconservative model was anticipated by Nikolai Koltsov and later supported by the Meselson-Stahl experiment which confirmed that DNA replicated semi-conservatively by conducting an experiment using two isotopes.
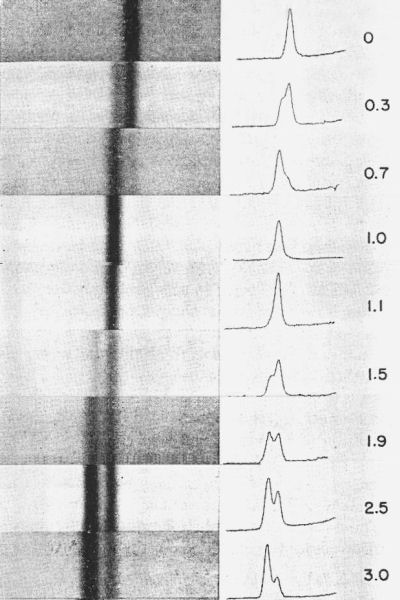
The MillerUrey experiment or Miller experiment is a famous chemistry experiment that simulated the conditions thought at the time 1952 to be present in the atmosphere of the early prebiotic Earth in order to test the hypothesis of the chemical origin of life under those conditions. The experiment deciphered the first of the 64 triplet codons in the genetic code by using nucleic acid homopolymers to translate specific amino acids. 15 N heavy and 14 N normal are two isotopes of nitrogen which can be distinguished based on their densities by centrifugation in Caesium chloride CsCl.
Double Helix and Pulse-Chase Experiment Educator Cheryl Coronado discusses how she uses the short film The Double Helix to introduce her students to how DNAs structure was uncovered. The MeselsonStahl experiment is an experiment by Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl in 1958 which supported Watson and Cricks hypothesis that DNA replication was semiconservative. Nitrogen is a key component of DNA and can exist as a heavier 15 N or a lighter 14 N.
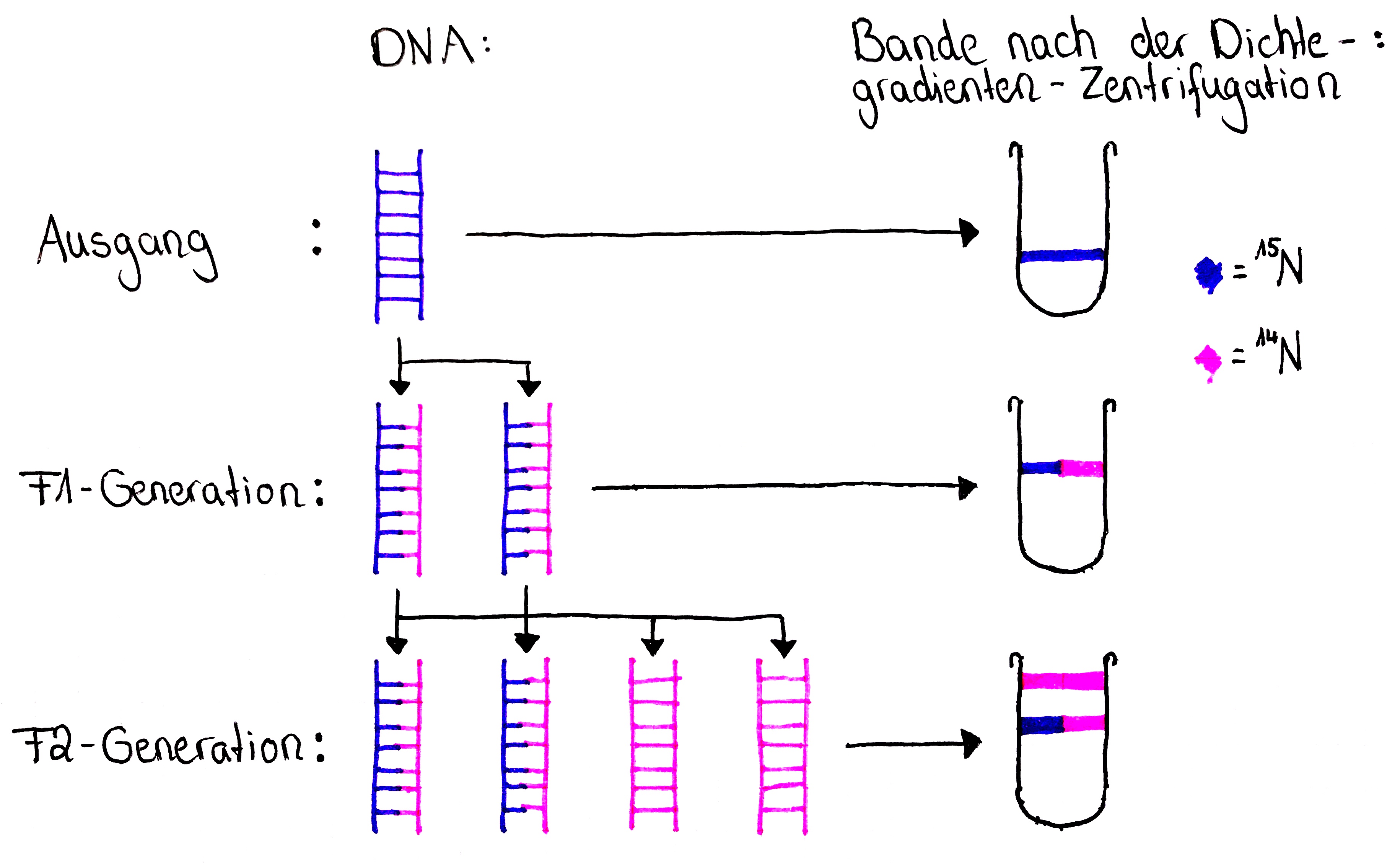
While DNA had been known to biologists since 1869 many scientists still assumed at the time that proteins carried the information for inheritance because DNA appeared to be an inert molecule and since it is located in the nucleus its role was considered to be phosphorus storage. Meselson and Stahl cultured Ecoli in a medium constituting 15 NH 4 Cl over many generations. As a result 15 N was integrated into the bacterial DNA.
In semiconservative replication when the double-stranded DNA helix is replicated each of the two new double-stranded DNA helices consisted of one strand from. A second version of the central dogma is popular but incorrect. The Physical Aspect of the Living Cell is a 1944 science book written for the lay reader by physicist Erwin SchrödingerThe book was based on a course of public lectures delivered by Schrödinger in February 1943 under the auspices of the Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies where he was Director of Theoretical Physics at Trinity College Dublin.
Das liegt daran dass im 14 N-Medium nur noch 14 N-Isotope eingebaut werden können. She then follows with the accompanying pulse-chase student activity that describes the experiment that proved DNA replication is semi-conservative. Nach der ersten Replikation entstehen DNA-Stränge mit einem 15 N-Mutterstrang und einer 14 N-Kopie.
Multiple experiments were conducted to determine how DNA replicates. Later they revised the 15 NH 4 Cl. 7 77933 LahrSchwarzwald 07821- 919 630 postscheffel-gymnasiumde.
In their experiments Hershey and Chase showed that when bacteriophages which.

The Meselson Stahl Experiment Learn Science At Scitable

Meselson Stahl Experiment Hilfe Qwq Biologie
Meselson Stahl Experiment 1958

Meselson Stahl Experiment Flashcards Quizlet
Folge 034 Das Meselon Stahl Experiment Genetik Teil 6
Folge 034 Das Meselon Stahl Experiment Genetik Teil 6
![]()
Das Meselson Stahl Experiment In Biologie Schulerlexikon Lernhelfer

Semi Conservative Bioninja
Meselson Stahl Experiment Ziel Ablauf Und Erkenntnisse Mit Video

State The Aim And Describe Meselson And Stahl S Experiment India Site
Wie Funktioniert Die Replikation Meselson Stahl Experiment Biologie

Meselson Stahl Experiment 1958 Abbildung Us Genetiker Matthew Meselson Geb 1930 Und Franklin Stahl Geb 1929 Fuhren Ihre Beruhmten 19 Stockfotografie Alamy

Datei Meselson Stahl Experiment Diagram En Svg Wikipedia
Solved Ap Bio Assignment About Dna Replication Meselon Stahl Experiment Course Hero
Nucleic Acids And The Genetic Material Problem Set

Pulse Chase Primer The Meselson Stahl Experiment
Molekularbiologie Der Zelle Teil 9 Dna Replikation Internet Evoluzzer